AES Chile Submits EIA for $10B Green Hydrogen and Ammonia Project
AES Chile has submitted the Environmental Impact Study (EIA) for the INNA project, its first industrial-scale green hydrogen and ammonia initiative in the country. The project, located in Taltal, Antofagasta region, which is in an initial development stage, is aligned with Chile's National Green Hydrogen Strategy.
"Although this project is in an early stage of development and the investment decision will have to be made later, the presentation of the EIA is a fundamental step to ensure the viability of the initiative," said Javier Dib, General Manager of AES Andes.
"AES Chile is accelerating the future of energy, creating opportunities that diversify Chile's energy matrix and support the country's sustainable energy goals. As with all of our projects, our partnership with local communities and stakeholders is a priority. We want to strengthen local development, while maintaining the highest environmental and safety standards," Dib continued.
To support this project, a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) was signed between AES Andes and Samsung C&T, a major Korean company with experience in energy and construction, which was recently awarded the contract for the first green ammonia receiving terminal in Korea.
The two companies are currently evaluating the joint development of the project, focusing on opportunities to produce green hydrogen for domestic consumption or for export to international markets.
The project submitted to the SEA includes the production of green hydrogen and ammonia, as well as the development of solar, wind and battery storage energy, in line with the needs of the project and to support the country's electricity generation.
"The company has carried out dedicated community engagement work with special attention to the Chango communities present in the area, as well as other relevant actors. We will maintain this commitment to collaborative work as we move forward with the environmental processing of Inna," said Luis Sarrás, Vice President of International Green Hydrogen at AES.
About AES ANDES
AES Andes generates and sells energy in Chile, Colombia and Argentina. The company operates 5,737 MW in South America along with a broad portfolio of renewable energy projects under development. The company is one of the leading generating firms in the region, with a diversified portfolio that includes hydroelectric, wind, solar, energy storage, natural gas and coal plants.
In Chile, AES Andes and its subsidiaries own and operate 3,965 MW, consisting of 1,645 MW of thermoelectric, 771 MW of hydroelectric, 431 MW of wind, 667 MW of solar photovoltaic, and 451 MW of battery energy storage systems, as well as seawater desalination plants and transmission lines.
'New Energy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 天気予報の手法で革新!水電解電極材料の劣化を短時間で予測 (0) | 2024.12.26 |
|---|---|
| China’s first seawater project (0) | 2024.12.26 |
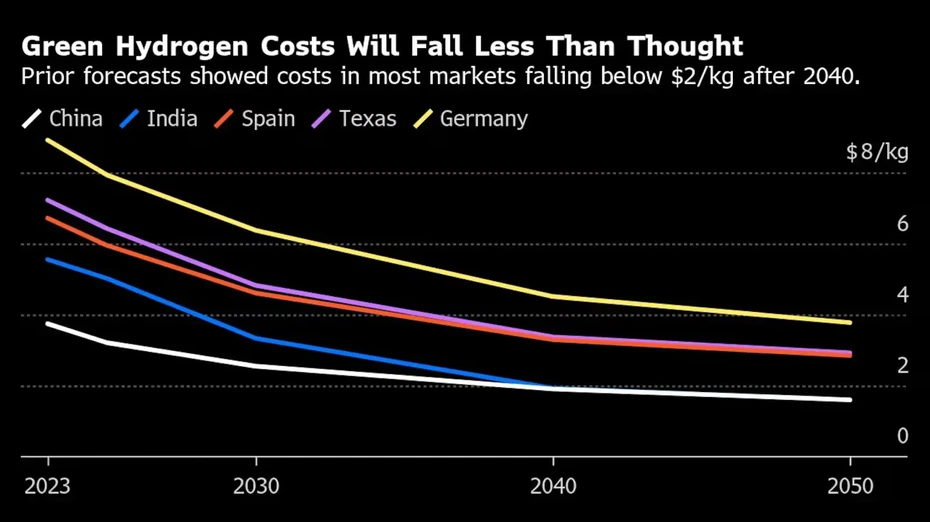
| Green Hydrogen Prices Will Remain Stubbornly High for Decades (0) | 2024.12.24 |
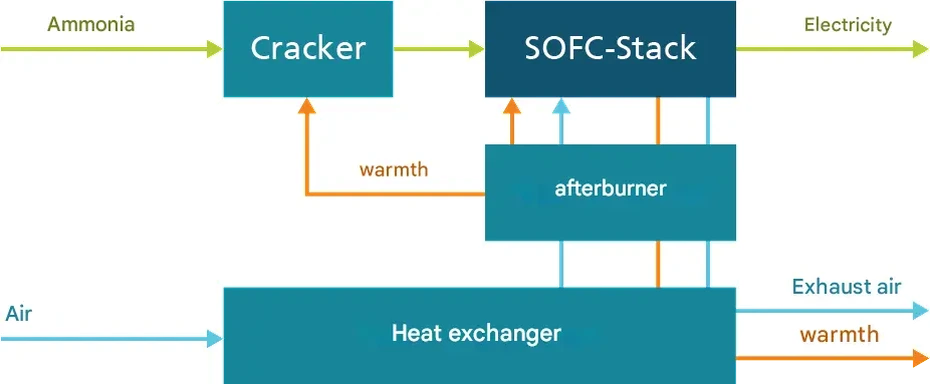
| Fraunhofer’s NH3 System Hydrogen Technology: Unlocking Climate-Friendly Electricity From Ammonia (1) | 2024.12.20 |
| US blue hydrogen to gain ground in 2025 as green hydrogen faces headwinds (0) | 2024.12.18 |