Dalian Institute of Chemicals has developed the first hydrogen anion prototype battery in China
Recently, the team of researchers Chen Ping, Cao Hujun, and Zhang Weijin, associate researchers from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made important progress in the development and application of hydrogen anion conductors. The team developed a new core-shell structure hydrogen anion electrolyte and successfully built the first hydrogen anion prototype battery. The relevant results were published in Nature on September 17, Beijing time.
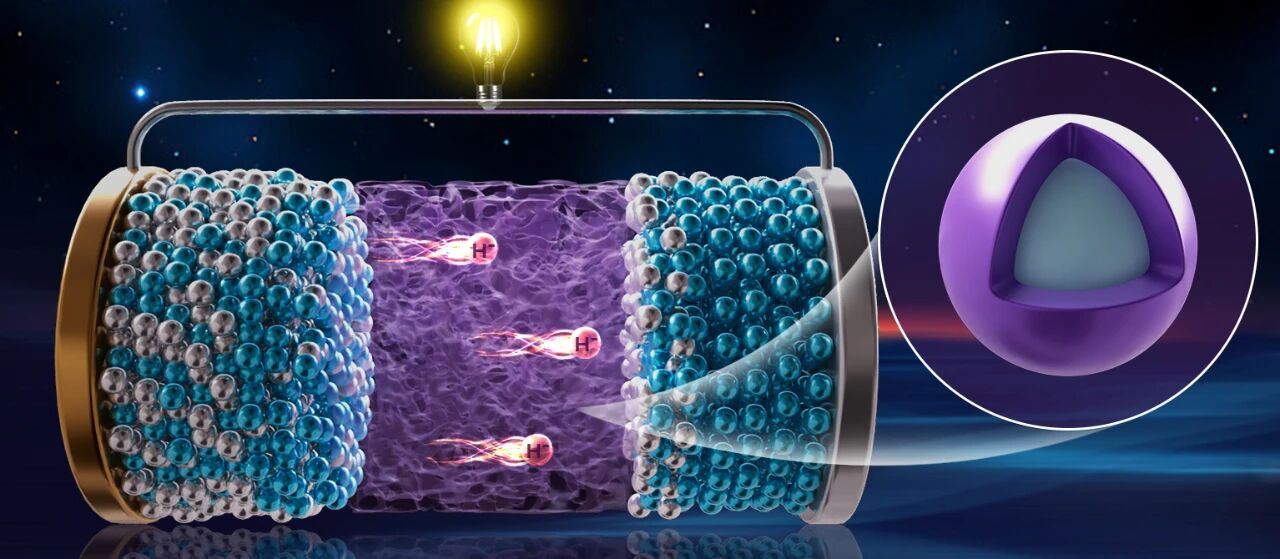
Hydrogen is considered an important part of the future clean energy system, usually in the form of hydrogen cations (protons), hydrogen anions and hydrogen atoms. Among them, hydrogen anion has the highest electron density, is easily polarized and the most reactive, and is a unique energy carrier with great potential. Hydrogen anionic batteries are an important research direction in this field. Similar to the widely used lithium-ion batteries today, hydrogen anionic batteries use the movement of ions to store and release energy. The difference is that the internal "porter" of this type of battery is no longer lithium ions, but hydrogen anions. However, due to the lack of electrolyte materials that can meet both high ionic conductivity, low electronic conductivity, excellent thermal stability and electrochemical stability, and good compatibility with electrode materials, hydrogen anion batteries are still in the concept stage, and their research and development has important scientific significance and application prospects.

In 2018, the team launched hydrogen anion conduction research, and in 2023, it proposed the strategy of "lattice distortion suppression electron conductance" to develop room-temperature ultrafast hydrogen anion conductors. On this basis, the team coated a thin layer of low electron conduction and high stability with low electron conduction and high stability of cerium trihydride (CeH3) to form a new core-shell structure composite hydride (3CeH3@BaH2), which can exhibit rapid hydrogen anion conduction characteristics at room temperature, and has excellent thermal stability and electrochemical stability, making it an ideal electrolyte material.
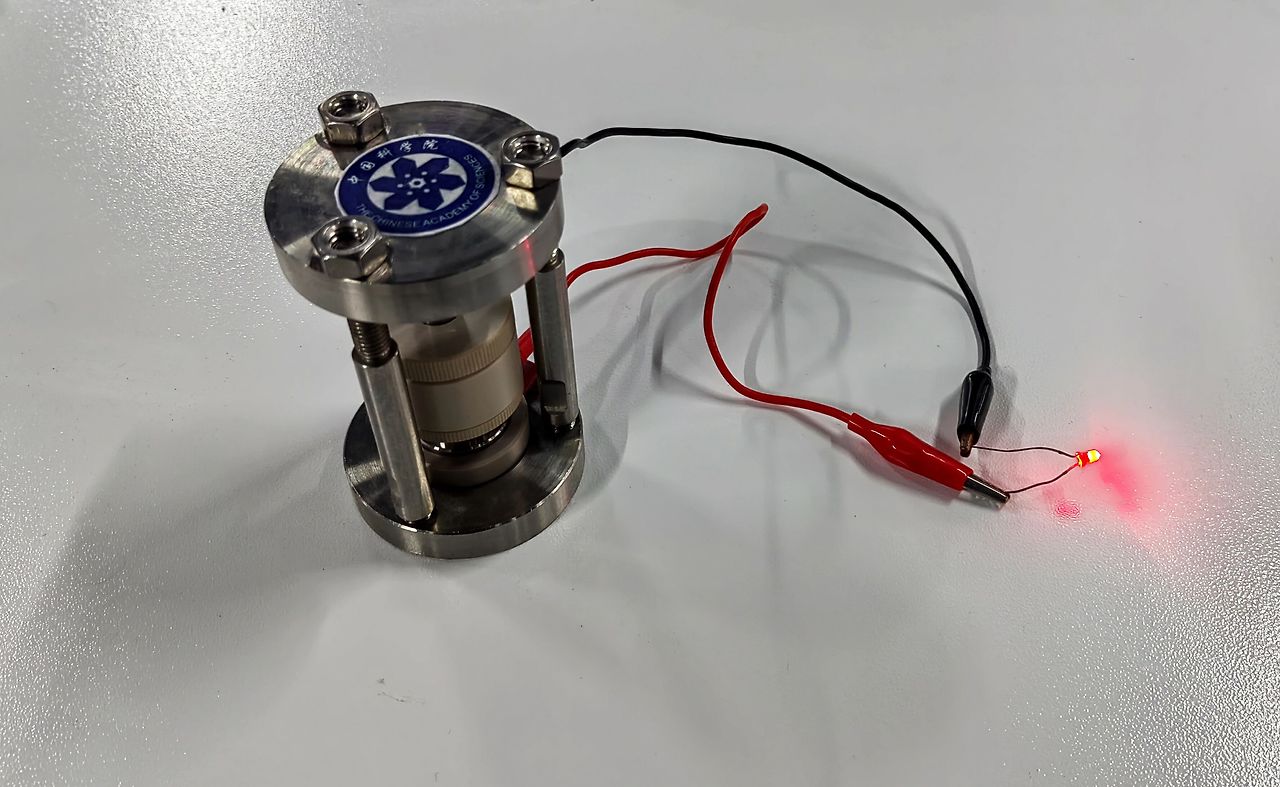
Based on the above-mentioned new hydrogen anion electrolyte material, the team used the classic hydrogen storage material sodium aluminum hydride (NaAlH4) as the positive electrode and the hydrogen-poor cerium dihydride (CeH2) as the negative electrode to assemble CeH2|3CeH3@BaH2| NaAlH4 is a hydrogen negative ion prototype battery. Experimental data show that the positive electrode of the battery has a capacity of up to 984 mAh/g (milliampere-hour/gram) for the first time, and can still maintain a capacity of 402 mAh/g after 20 charge-discharge cycles. The team further built a stacked battery, increased the voltage to 1.9 volts, and successfully lit a yellow LED light, proving the feasibility of hydrogen anion batteries to power electronic devices. This marks that our country's researchers have achieved a leap from "principle concept" to "experimental verification" of hydrogen anion batteries.
Hydrogen anionic batteries represent a new energy storage technology path, which is expected to play an important role in large-scale energy storage, hydrogen storage, mobile power supplies, special power supplies and other fields. In the future, the team will focus on the development of core materials and performance optimization of hydrogen anion batteries, actively expand application scenarios, and provide strong technical support for our country's green energy development.
大连化物所研发出国内首例氢负离子原型电池 - 市场动态 - 氢启未来
作者:官方 来源:互联网 所属栏目:市场动态 发布时间:2025-09-22 09:11 [ 导读 ]近日,中国科学院大连化学物理研究所陈萍研究员、曹湖军研究员、张炜进副研究员团队在氢负离子导体开发及其应用方
www.h2weilai.com

