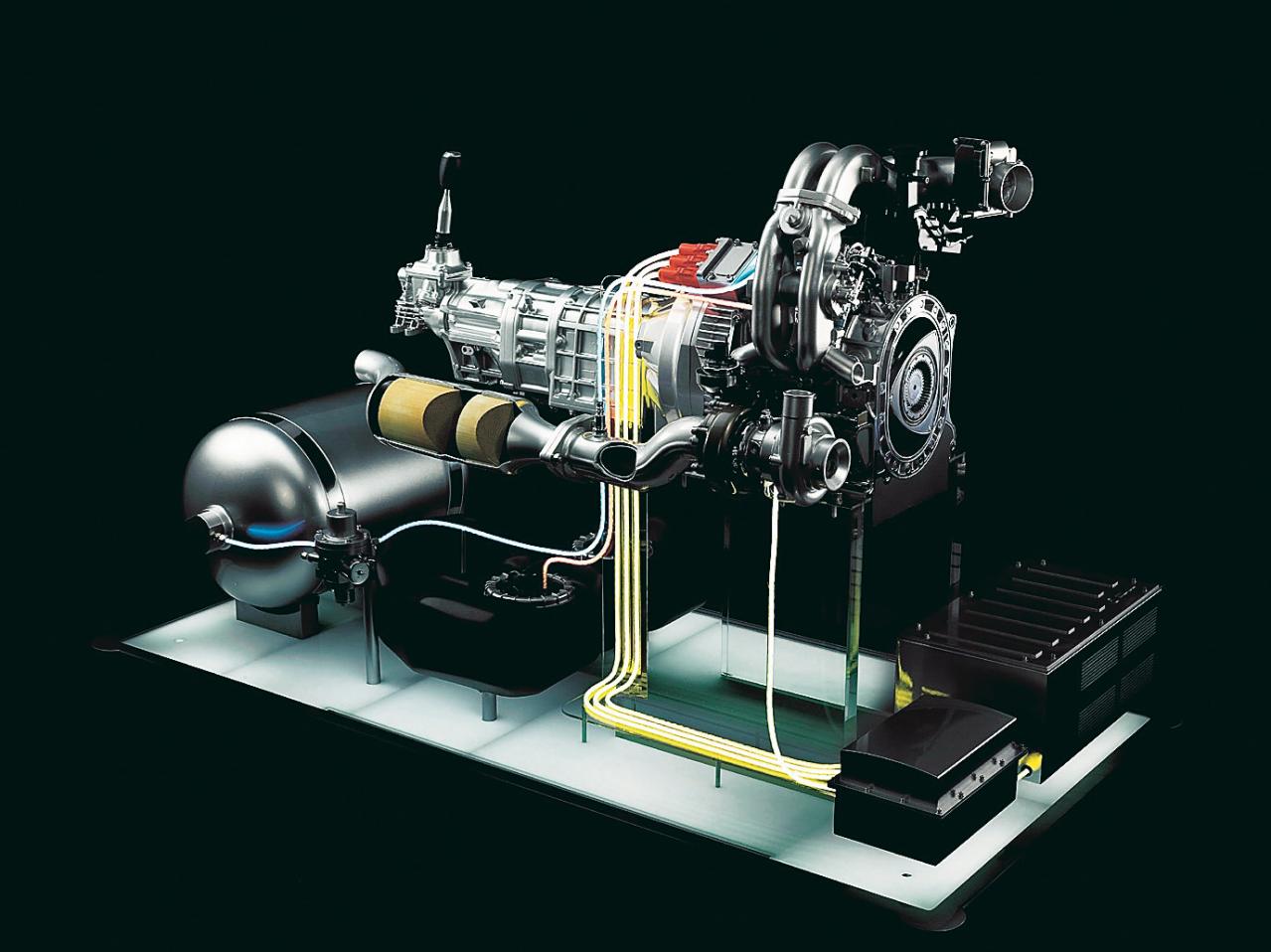
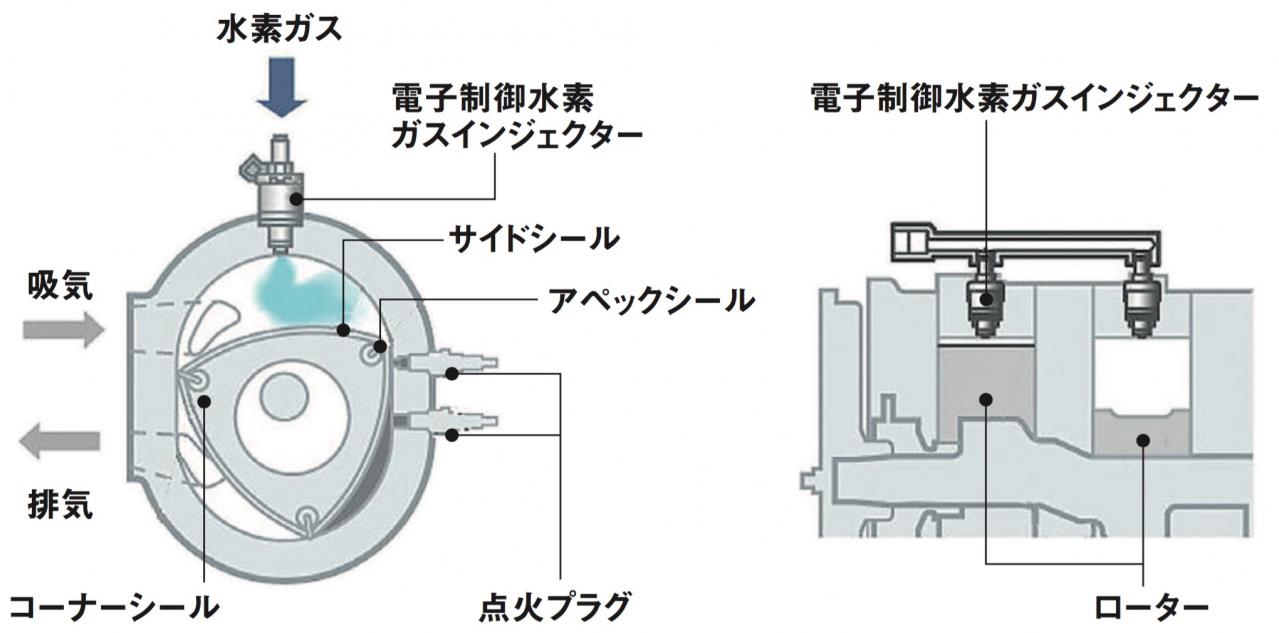
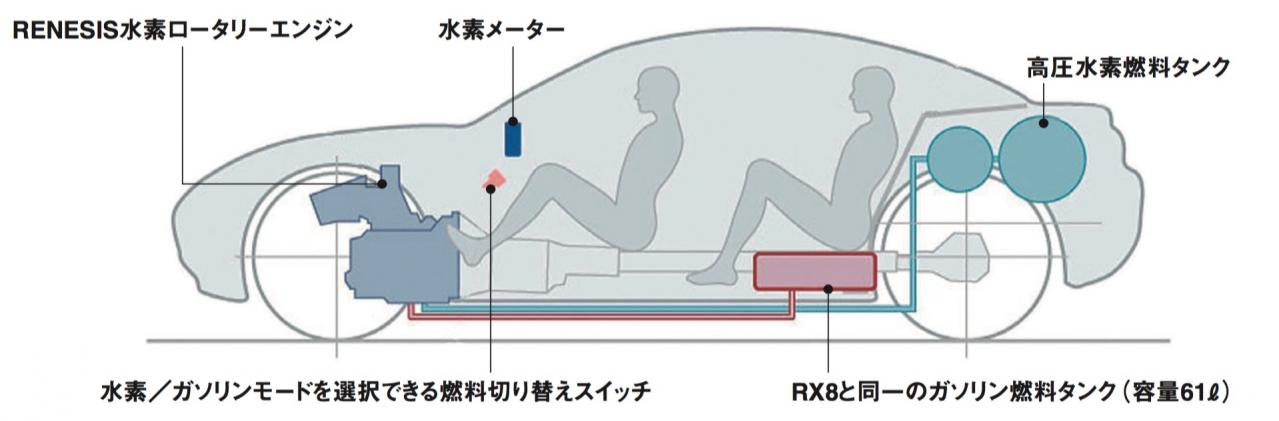
Europe is going all in on hydrogen power. Why isn’t the US?

This post has been updated with a correction.
Once upon a time, hydrogen was supposed to be the future of energy. In 1845, English scientist Sir William Grove (aka “the father of the fuel cell”) demonstrated that, given the right conditions and the addition of oxygen, hydrogen gas — also called H2 — can undergo a chemical reaction and produce a potent, and non-polluting, electrical punch. The possibilities for hydrogen power seemed endless: It could fuel our cars, heat our homes, and even power our airplanes. But today, 175 years after the creation of that first “gas battery,” the technology has yet to reach its full potential.
True, some of hydrogen power’s initial promise has borne fruit — there are cars running on compressed hydrogen cells (producing a trickle of water instead of toxic exhaust) and even some small H2-powered planes in development. But with more and more cars using lithium-ion batteries instead — and airlines developing sustainable fuels made from cooking oil and mustard seed — it’s probably not going to happen anytime soon.
There’s one sector, however, where hydrogen power could be critically important: manufacturing, the part of the economy that makes steel, cement, and basically every other material good. Industrial processes, most of which involve burning fossil fuels on-site for energy, account for over 20 percent of fossil fuel pollution worldwide. Those emissions are notoriously difficult to cut, but experts say that hydrogen, produced with renewable energy, could provide a solution.
“Hydrogen is probably the most promising” way to cut industrial emissions, said Kobad Bhavnagri, head of special projects at BloombergNEF, an independent research firm focusing on clean energy. “It’s the most versatile and the most scalable solution to getting to zero emissions.”
Now, normally, H2 isn’t exactly a “clean” form of energy. Although hydrogen is a naturally occurring element, it needs to be treated in order to produce the kind of highly pure stream necessary for fuel cell production. In the U.S., 95 percent of hydrogen is manufactured through a process called “steam reforming,” in which natural gas is combined with steam and then broken into its component parts, including hydrogen and carbon dioxide. (Not only does the reaction produce CO2 on its own, but the process also requires a whole bunch of energy which is not great for the planet.) But hydrogen can also be made cleanly out of regular old water (H2O — makes sense, right?) and electricity. If the electricity comes from renewable sources like wind or solar, the resulting fuel is called “green hydrogen.”
“It’s not rocket science,” said Thomas Koch Blank, senior principal of industry and heavy transport at the Rocky Mountain Institute. “It’s basically a big bathtub, and you stick a power cord at each end and run a current through it.” The electric current splits the water into O2 and H2, and voila! green hydrogen is born.” (Note: Kids, don’t try this at home.)
Green hydrogen could be crucial to decarbonizing industrial manufacturing. In most sectors, the solution to cutting emissions is to electrify everything — cars, for example, or home heating. But for, say, concrete production, that classic formula doesn’t work. Industrial processes require high levels of heat and complicated chemical reactions that can’t be provided by electricity alone. Hydrogen, on the other hand, can burn hot enough to run a blast furnace, and also be used as an ingredient in necessary chemical processes for products like steel.
At the moment, this is all fairly speculative — industry still runs mostly on fossil fuels. But in the wake of the global COVID-19 pandemic, European countries are boosting green hydrogen programs as part of their coronavirus stimulus packages, positioning themselves as leaders in a largely untapped market. Last month, Germany announced a “National Hydrogen Strategy,” earmarking $8.2 billion for investments in new business and research around green hydrogen, and an additional $2.3 billion for building up international partnerships around the new fuel.
The European Union as a whole hasn’t announced a green hydrogen spending plan yet, but it has promised to prioritize the gas in the coming decades. The European Commission announced earlier this month that it would aim to deploy 40 gigawatts of electrolyzers (the machines that split water into hydrogen and oxygen) within its borders by 2030 and another 40 in countries that can export to the EU. That represents about 320 times the electrolyzing power currently available worldwide.
“What Europe and Germany have done, I suspect, will trigger something of an arms race or a scale-up race” for hydrogen power, Bhavnagri told Grist. “Everybody else will now have to get on board if they want to keep pace.”
The United States, however, is dragging its feet. “The U.S. at a national level has not released any hydrogen strategy,” Bhavnagri said.
U.S. investments in green hydrogen have been small thus far: The Energy Department announced last week that it would spend $64 million on hydrogen research and development in 2020, with $15 million earmarked towards lowering the cost of green hydrogen specifically. But that $64 million is still only a tiny fraction of what Germany has vowed to spend boosting its own H2 technology.
Meanwhile, House Democrats’ massive, 538-page climate plan mentions green hydrogen, but stops short of recommending specific investments or a large-scale build out of electrolyzing technology across the country. Instead, Democrats simply point to the need for a tax credit to lower production costs for low- or zero-emission hydrogen projects. This is despite the fact that, according to modeling from the nonpartisan policy firm Energy Innovation, switching industrial fuels to green hydrogen could reduce U.S. greenhouse emissions by roughly a billion tons by 2050 — equivalent to taking around 200 million cars off the road for a whole year.
According to Blank, the United States’ slow progress on green hydrogen is partly due to the widespread availability of natural gas, which, although it produces fewer emissions than coal or oil, is associated with other environmental risks. “For the U.S., natural gas equals energy security,” he said. With abundant — and cheap — fossil fuels within its borders, the U.S. doesn’t have much incentive to make the leap to hydrogen. “Without carbon prices, it’s a stretch to see that hydrogen is going to be competitive on any large scale,” Blank said of the U.S. industrial sector.
In Europe, on the other hand, the geography and geology is more conducive to a hydrogen power. There are huge areas in the North Sea ideally situated for offshore wind turbines, which could make the production of green hydrogen more economical. Europe also lacks substantial reserves of natural gas, compounding the need for alternative fuel sources that can be manufactured within the bloc itself.
The result, according to Bhavnagri, will be a world that increasingly looks to Europe for hydrogen manufacturing systems — leaving the United States in the dust. For green hydrogen, he warned, “you will go to the European players.”*
*Correction: This piece initially stated that American firms like General Electric would not be sought out for expertise on green hydrogen. In fact, the company is doing advanced work on hydrogen.
https://grist.org/energy/europe-is-going-all-in-on-hydrogen-power-why-isnt-the-us/
'Fuel Cell' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Fuel cell company makes STAR Market debut (0) | 2020.08.11 |
|---|---|
| Fuel cell electric vehicles powered by Ballard have driven more than 50M km; 70% in China (0) | 2020.08.10 |
| Plug Power planning new 'gigafactory,' although location undecided (0) | 2020.08.07 |
| Why Plug Power Stock Is Soaring 17% Today (0) | 2020.08.07 |
| DLR and MTU Aero Engines study fuel cell propulsion system for aviation (0) | 2020.08.07 |